Evidence-Based Design Workshop
- Deanne Watt
- Jun 17, 2025
- 2 min read
Evidence-based design (EBD) offers a structured approach to making design decisions that are rooted in data and research rather than intuition or fleeting trends. This methodology not only enhances user experience but also drives innovation, reduces development costs, and accelerates project timelines by ensuring that products meet the real needs of users. Unlike a one-off workshop, EBD is an ongoing reference exercise that integrates seamlessly into the design process, providing a framework for continuous improvement and value generation.
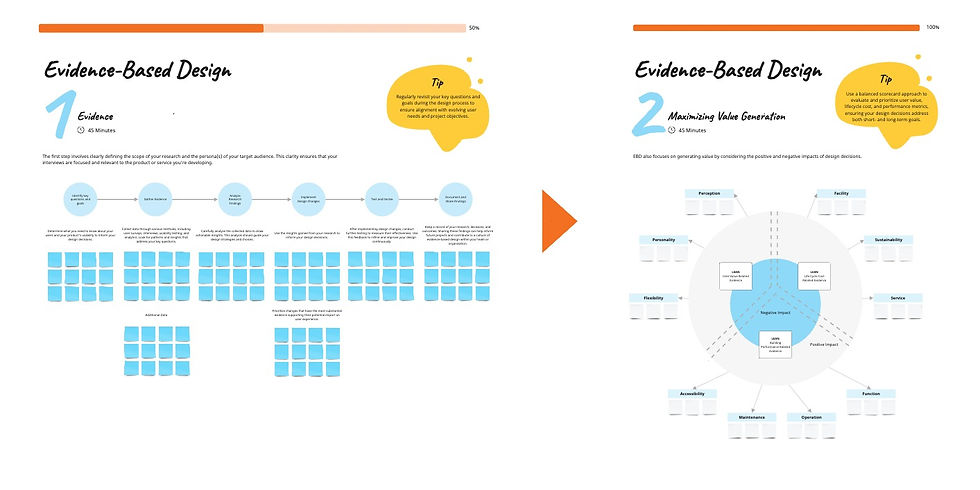
EBD transforms the design process into a data-driven exercise, where every decision is supported by concrete evidence. This approach has two major components:
Part 1
The Evidence-Gathering Process
Identify Key Questions and Goals: Begin by defining the objectives of your design process. What user needs are you addressing? What challenges are you aiming to overcome?
Gather Evidence: Collect data through various methods such as user behavior analytics, usability studies, A/B testing, and user interviews. This evidence forms the basis of your design decisions.
Analyze Research Findings: Delve into the data to uncover insights about user preferences, pain points, and behaviors. This analysis will guide your design strategy.
Implement Design Changes: Use the insights gained from your research to inform design updates and enhancements. This iterative process ensures that your design evolves in response to user needs.
Test and Iterate: Continuously test your design with real users to validate changes and gather more data, which will inform further iterations.
Document and Share Findings: Keep a detailed record of your findings, decisions, and outcomes. Sharing this knowledge can inform future projects and contribute to a culture of evidence-based practice.
Part 2
Maximizing Value Generation
EBD also focuses on generating value by considering the positive and negative impacts of design decisions. This involves analyzing:
User Value-Related Evidence: Understand how your design affects user perception, personality, and flexibility. This insight helps create interfaces that resonate with users on a personal level.
Life Cycle Cost-Related Evidence: Consider factors like facility, sustainability, and service to ensure that your design is not only effective but also efficient over its lifecycle.
Building Performance-Related Evidence: Evaluate your design's accessibility, maintenance, operation, and function to ensure it performs optimally in various contexts.
This comprehensive view allows designers to see the connection between evidence-based design and lean outputs, highlighting how informed decisions can lead to more effective, efficient, and user-centered products.
Evidence-based design is not just a methodology; it's a mindset that prioritizes data and research over assumptions and trends. By embedding EBD into the UI/UX design process, designers and teams can create products that truly resonate with users, stand the test of time, and lead the market. As an ongoing exercise, EBD encourages continuous learning, adaptation, and improvement, ensuring that design decisions contribute to the creation of exceptional user experiences and the achievement of business goals. Embrace EBD to transform your design process into a powerful engine for innovation and value creation.